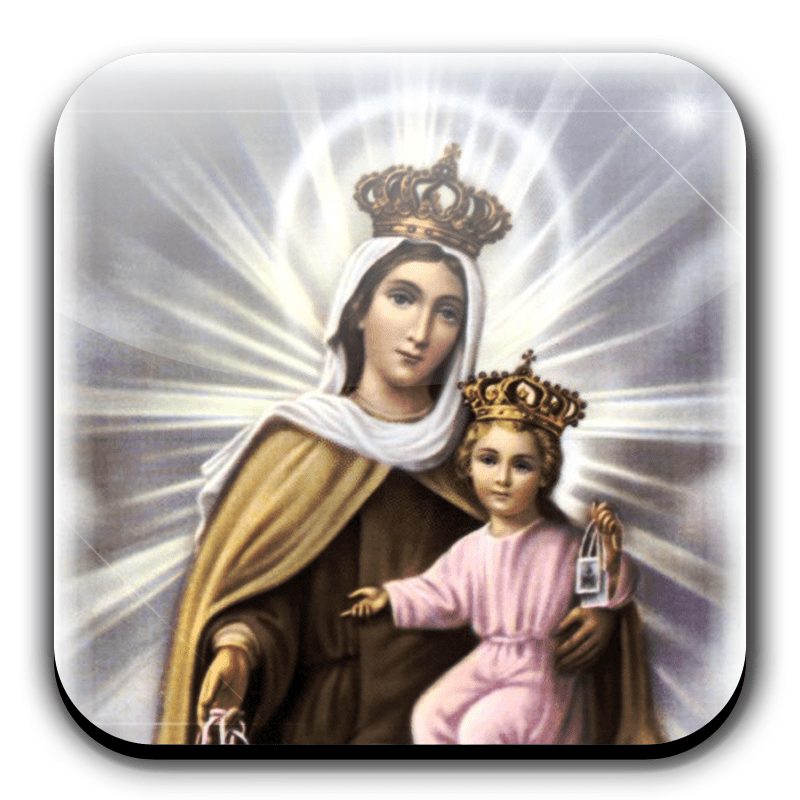
The feast of Our Lady of Mount Carmel was first instituted in the late 14th century in commemoration of the approval of the rule of the Carmelite Order a hundred years earlier. According to legend, a religious community was established even before the time of Christ on Mount Carmel. This is the mountain overlooking the Mediterranean Sea on which the prophet Elijah successfully challenged the priests of Baal and won the people to the true God. The feast of Our Lady of Mount Carmel entered the Calendar of the universal Church in the early 18th century.
The feast of Our Lady of Mount Carmel was first instituted in the late 14th century in commemoration of the approval of the rule of the Carmelite Order a hundred years earlier. According to legend, a religious community was established even before the time of Christ on Mount Carmel. This is the mountain overlooking the Mediterranean Sea on which the prophet Elijah successfully challenged the priests of Baal and won the people to the true God. The feast of Our Lady of Mount Carmel entered the Calendar of the universal Church in the early 18th century.
Although there is no historical evidence for the pre-Christian Carmelite community, references in the 12th century record a community of monks on the holy mountain. Despite continual difficulties, the community built a monastery and church dedicated to the Virgin Mary on Mount Carmel in 1263. Saint Louis, King of France, had visited Mount Carmel in 1254, and brought back six French hermits for whom he built a convent near Paris. Mount Carmel was taken by the Saracens in 1291, and the brothers were killed and the convent burned. The spread of the Carmelites in Europe is largely attributable to the work of Saint Simon Stock (1247-65). The Carmelite Order was formally approved in 1274 at the Council of Lyon.
Among the best known Carmelites today are two women: Saint Theresa of Jesus (Theresa of Avila – 1515-1582) who despite many difficulties reformed the Carmelite Order (the Discalced Carmelites); and Saint Edith Stein (Theresa Benedicta of the Cross – 1891-1942), a Jewish convert and philosophy professor, who was killed at Auschwitz, canonized in 1998, and proclaimed “co-patroness” of Europe in 1999.