Perhaps nowhere in the history of the Church is there a better example of a man possessed of so many of the saintly virtues—piety, charity, deep humility, pastoral zeal, and simplicity—than in one of the newest of God’s elect, St. Pius X. Yet the parish priest of Tombolo, who remained a country priest at heart throughout his life, faced the problems and evils of a strife-torn world with the spiritual fervor of a crusader. The inscription on his tomb in the crypt of the basilica of St. Peter’s gives the most eloquent testimony to a life spent in the service of God:
“Born poor and humble of heart,
Undaunted champion of the Catholic faith,
Zealous to restore all things in Christ,
Crowned a holy life with a holy death.”
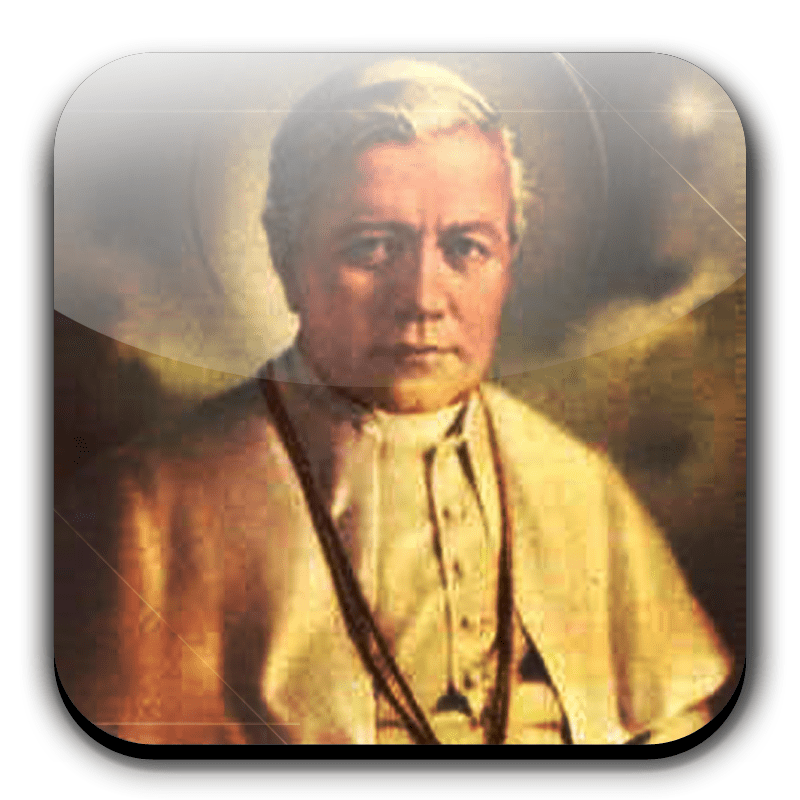
St. Pius X was born Giuseppe Melchiorre Sarto on June 2, 1835 in the little Italian town of Riese, in the province of Treviso near Venice. His father was Giovanni Sarto, a cobbler by trade, who was also caretaker of the city hall and the town’s postmaster; his mother was Margherita Sanson, a seamstress. The family had few worldly goods and the early life of young Giuseppe, eldest of eight surviving children, was a difficult one. He attended the parish school and while there, his intelligence and high moral character attracted the notice of the pastor, who arranged a scholarship for the lad at the high school in Castelfranco, a larger town two miles from Riese. After completing the course of instruction at Castelfranco, he made known that he had felt the call to the priesthood for some time, but had considered the means of attaining this end beyond his grasp. However, his parents saw that the will of God was in their son’s calling, and they did all in their power to encourage him, while the pastor again came to the rescue by arranging another scholarship to the seminary at Padua. In November of 1850, young Sarto arrived at Padua and was immediately taken up with the life and studies of the seminary. The same high qualifications of intellect and spirit, later to blossom forth in his work as bishop and Pope, were much in evidence as a seminarian. Giuseppe worked hard and finally on September 18, 1858, Father Sarto was ordained at the cathedral in Castelfranco.
The young priest’s first assignment was as curate at Tombolo, a parish of 1500 souls in the Trentino district of Italy. Here, for eight years, Father Sarto labored among his favorite parishioners, the poor. He also organized a night school for the general education of adults, and trained the parish choir to a high degree of skill in Gregorian Chant. His pastor at Tombolo, Father Constantini, recognizing the worth of the young priest, wrote a prophetic summary of his assistant. “They have sent me as curate a young priest, with orders to mould him to the duties of pastor; in fact, however, the contrary is true. He is so zealous, so full of good sense, and other precious gifts that it is I who can learn much from him. Some day or other he will wear the mitre, of that I am sure. After that—who knows?”
In July of 1867, Father Sarto, then 32 years of age, was appointed pastor of Salzano, one of the most favored parishes in the diocese of Treviso. Soon his concern and help toward the poor became well known throughout the parish, and his two sisters, who acted as his housekeepers, were often at wit’s end as their brother gave away much of his own clothing and food to the needy. The new pastor arranged for the instruction of young and old in the fundamentals of Christian Doctrine. The firm conviction that devotion meant little if its meaning was not understood was later to be embodied in the encyclical <Acerbo nimis>, “On the Teaching of Christian Doctrine.” After nine years at Salzano, Father Sarto was rewarded for his labors by the appointment as Canon of the Cathedral at Treviso and as Chancellor of that diocese. In addition, he became Spiritual Director of the seminary. Canon Sarto took a deep interest in this work of forming Christ in the hearts of young priests. However, in spite of these many duties, he remained ever the teacher; he often journeyed from the seminary into the city to teach catechism to the children, and he organized Sunday classes for those children who attended public schools, where religion was banned. When the diocese of Mantua fell vacant in 1884, Pope Leo XIII named Canon Sarto as bishop of that diocese.
Bishop Sarto found a troubled diocese in which to begin his labors. There was a general opposition of the government to religion manifested in many ways—monasteries had been suppressed, many religious institutions were government-managed, and Church property was heavily taxed. All these political disturbances had a far-reaching effect on both the clergy and the laiety. The seminaries of Mantua were depleted and a general laxity among the younger priests was evident; dangerous errors of thought had crept into the clergy, and the faults of the shepherds had spread to the flock. In general, a pall of religious indifference and secularism had spread over the diocese. With characteristic energy and spiritual strength, Bishop Sarto set to work to put his see in order. He gave first attention to the seminary, where by his own example of zeal and teaching, he won back the clergy to full and faithful service. The laxity of the people was attributed to neglect of parish priests in the instruction of the catechism; Bishop Sarto often taught such classes himself, and in his pastoral visits and letters, he urged the establishment of the Confraternity of Christian Doctrine in all parishes. God blessed this work on behalf of all classes of His flock, and in 1893, His Holiness, Leo XIII, elevated Bishop Sarto to Cardinal and appointed him Patriarch of Venice.
As Patriarch of Venice, it was Tombolo, Salzano, and Mantua all over again, but on a widening scale—the same care for his clergy and for the seminaries, the ever-willing hand and heart given to the poor, the long hours spent in teaching young and old—only the red of his new office had replaced the purple and black of former days. Social and economic problems were of prime concern to the new cardinal, and any worthy social action organization was assured of his help. When the Workingmen’s Society was founded in Venice, the name of Cardinal Sarto was at the top of the list and he paid regular dues as a member! Once it seemed that an important diocesan newspaper would go into bankruptcy, and the cardinal declared, “I would rather sell my crozier and my robes of office than let that paper go under.”
On July 20, 1903, the reign of Leo XIII came to a close, and the world mourned the death of a great Pontiff. Cardinals from all over the world came to Rome for the conclave which would elect the new Pope, and it is again typical of Cardinal Sarto that, due to his many charities, he was short of funds necessary to make the trip; so sure was he that he would never be elected that the problem was solved by the purchase of a return ticket to Venice! With the conclave in solemn session, the voting began, and with each successive ballot, Cardinal Sarto gained more votes. As his cause continued to gain strength, he all the more strongly pleaded that he was neither worthy nor capable enough for the office. When it was finally announced that he had gained sufficient votes to be elected, he bent his head, broke into tears, and whispered, “Fiat voluntas tua” (Thy will be done). He accepted, took the name of Pius X, and on August 9, 1903, was crowned as Vicar of Christ on earth.
The world was now the parish of the new Pontiff, and in his first encyclical he announced the aim of his reign. It was his desire, in the words of St. Paul, “to restore all things in Christ.” (Eph 1:10). The prime means of accomplishing this restoration was dearly seen by Pius to be through the clergy, and throughout his reign, the Pope exhorted bishops to reorganize the seminaries and to obtain the best possible training for these men who would instill in others the knowledge of God. The Pontiff published an encyclical, “Exhortation to the Catholic Clergy,” in which he pointed out that only through a trained and disciplined clergy could a program of return to Christ be realized.
The religious instruction of young and old became the second most important means toward the Christian restoration, and in his encyclical <Acerbo nimis>, “On the Teaching of Christian Doctrine,” Pius X firmly stated his position. The evils of the world were traceable to an ignorance of God, he said, and it was necessary for priests to make the eternal truths available to all and in a language that all could understand. Ever an example, he himself gave Sunday instruction to the people in one of the Vatican courtyards. However, no reform of Pius’ was more widely acclaimed than the Decrees on Holy Communion, and Pius X is often called “the Pope of the Eucharist.” These decrees, issued from 1905 through 1910, allowed the reception of first Holy Communion at an earlier age than had formerly been required, encouraged the frequent reception of the Holy Eucharist by all Catholics, and relaxed the fast for the sick.
In the field of Christian social action the Pope had always been an ardent champion, and in 1905, he published <Il fermo proposito>, “On Catholic Social Action.” In this work, the Pontiff listed practical recommendations for the solution of the social problem; he reaffirmed the need and power of prayer, but said that society would not be Christianized by prayer alone. Action is needed, he pointed out, as had been shown in the lives of the Apostles and of saints like Francis Xavier. The Pope likewise vigorously promoted reforms within the liturgy of the Church, since he felt that these were long overdue. In his <Motu proprio on the Restoration of Church Music>, he listed the aims of such music to be sanctity, beauty of form, and universality. Gregorian Chant, the Pope felt, was the music best suited to attain those aims. However, he felt that an attempt to make all Church music Gregorian was an exaggerated fad, and modern compositions were always welcomed by the Pontiff as long as they fulfilled the prescribed norms. Pius also reformed the Breviary, and was founder of the Biblical Institute for the advancement of scholarship in the study of the Scriptures. Even more important for the internal structure of the Church, he initiated and closely supervised the construction of the Code of Canon Law.
The familiar notion of Pius X as the Teacher of Christian Truth and the firm guide and staunch foe of error was forceably illustrated in 1907 when he issued more than fourteen pronouncements against the growth of Modernism. This subtle philosophy, in which Pius saw the poison of all heresies, pretended to “modernize” the Church and to make it keep pace with the changing times. In reality, its end would have been the destructions of the foundation of faith. The crowning achievement of the Pontiff’s writings and pronouncements against this philosophy came in the encyclical, <Pascendi dominici gregis>, “On the Doctrines of the Modernists.” In this work, which was a death blow to Modernism, he gave a systematic exposition of the errors involved, their causes, and provisions for combatting the errors by definite preventive measures.
Pius X labored for the Master until the very last days of his life. His 79 years had not set too heavily upon him, but overwork and anxiety over the impending doom of a World War began to take their toll. Pius saw clearly the horrors of the coming conflict and felt helpless that he could not prevent it. A little more than a month after the outbreak of the war, the Pope was seized with an attack of influenza, and his weakened constitution could not combat the illness. The end for the Christ-like Pius came peacefully on August 20, 1914, and the world, though in the throes of a death struggle, paused to mourn the gentle and humble man whose last will and testament gave such an insight into his character. It read, in part, “I was born poor, I lived poor, I die poor.” Shortly after his death, the faithful began to make pilgrimages to his tomb, bringing flowers, prayers, and petitions for favors. Accounts of miraculous favors and cures, some even accomplished during his lifetime and granted through his intercession, were announced and given widespread acclaim. In 1923, the Church, always cautious in such matters, began inquiry into the life and virtues of Pius X, and in February of 1943, the first official step in his Cause was taken when the necessary decree was signed by the present Pontiff, Pius XII. In honor of the work which Pius X had accomplished in its behalf, the Confraternity of Christian Doctrine actively contributed in promoting the Cause for his beatification and canonization. On June 3, 1951, Pius X was declared Blessed, and finally on May 29, 1954, amid the traditional pealing of the bells in the great churches of Rome, Giuseppe Sarto, the humble parish priest of the world, was canonized a saint of God.
















St. Pius, Please pray for me that I may live a life in accord with God’s will and That I along with my family will attain to spiritual perfection in full communion with the church. Ask God to grant me peace and joy through a more perfect union with Jesus and frequent reception of the Holy Eucharist! thank you, amen.
Pope St. Pius X, pray for us. I have been privileged on at least three occasions to celebrate the Holy Sacrifice of the Mass at the Altar in St. Peter’s Basilica in which the remains of St. Pius X are reposed. He was a favorite patron of my late mentor, who had a great devotion to him, especially due to his introduction of First Holy Communion at the age of reason. Let us pray that the custom of frequent, even daily reception of Holy Communion, advocated by Pope St. Pius X, may lead to greater faith in and devotion to Our Eucharistic Lord, present under the forms of bread and wine.
Pope St. Pius X, pray for the preservation of Tradition.
If you’re still on the fence: grab your favorite earphones, head down to a Best Buy and ask to plug them into a Zune then an iPod and see which one sounds better to you, and which interface makes you smile more. Then you’ll know which is right for you.